12 Essential Emergency Preparedness Tips
Being prepared for emergencies can make a significant difference in ensuring safety and security. Here are 12 essential tips for emergency preparedness:

1.
Create a Plan
Develop a family emergency plan that includes communication strategies and meeting points.
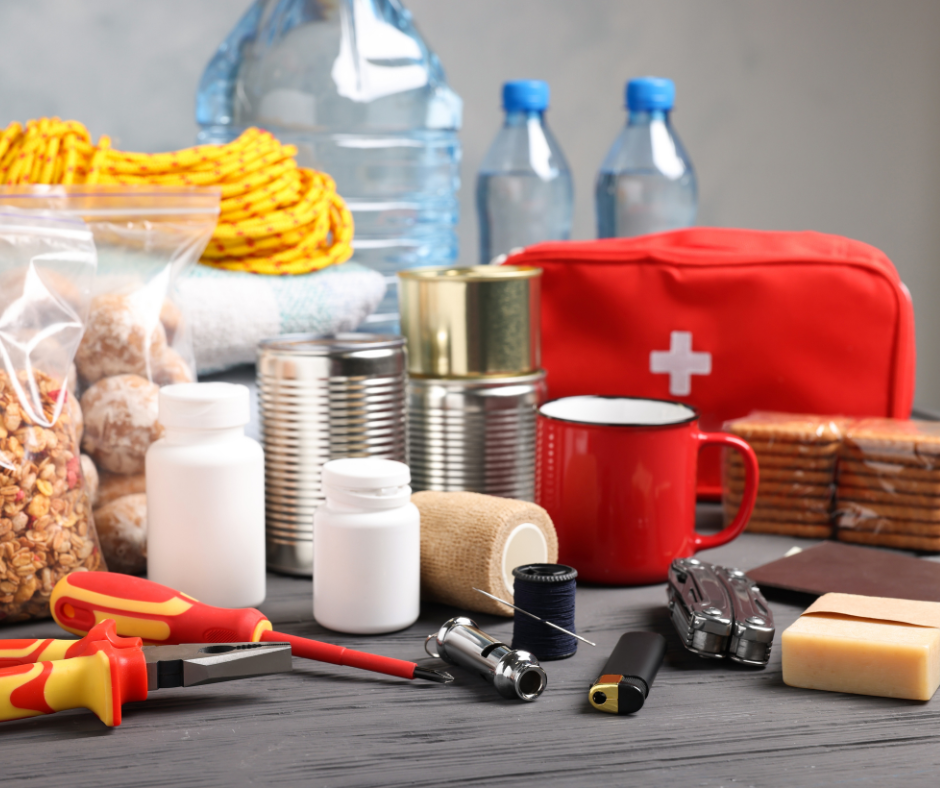

2.
Build an Emergency Kit
Assemble a supply kit with essentials like water, non-perishable food, medications, first aid supplies, flashlight, batteries, and important documents.

3.
Stay Informed
Keep updated on local emergency alerts and news through radio, TV, or emergency notification apps.

4.
Know Escape Routes
Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes from your home, workplace, and community.
5.
Practice Fire Safety
Install smoke alarms, have fire extinguishers, and conduct fire drills regularly.

6.
Prepare for Power Outages
Have alternative lighting sources (like flashlights and lanterns) and consider a generator if feasible.
7.
Learn Basic First Aid
Take a first aid and CPR course to be prepared to assist others in emergencies.

8.
Secure Your Home
Bolster home security with strong locks, window bars, and secure garage doors.

9.
Plan for Pets
Include provisions for your pets in your emergency kit and plan for their care during evacuations.

10.
Communicate with Neighbours
Get to know your neighbours and consider how you can support each other during emergencies.

11.
Maintain Insurance Coverage
Ensure your home and belongings are adequately insured against potential hazards.

12.
Review and Update Regularly
Regularly review and update your emergency plans, supplies, and contact information to stay prepared.
Emergency Self-Care Video Gallery

Fire Safety
Fire safety is paramount in both residential and commercial settings, crucial for protecting lives and property. Implementing effective fire safety measures begins with prevention. Ensuring smoke detectors are installed and regularly maintained can provide early warnings crucial for evacuation. Furthermore, having readily accessible fire extinguishers and knowing how to use them is essential. Developing and practicing a fire escape plan with all household or team members ensures everyone knows the safest routes out of the building. Additionally, keeping flammable materials properly stored and ensuring electrical systems are maintained and inspected regularly can significantly reduce fire risks. Finally, educating oneself and others about fire safety protocols and regularly conducting fire drills can prepare individuals to react swiftly and calmly in the event of a fire emergency. By prioritizing these measures, individuals and organizations can mitigate risks and ensure a safer environment for all.

Flood Safety
Flood safety is crucial for individuals and communities living in flood-prone areas or facing sudden inundation risks. Preparation begins with awareness and understanding of flood risks specific to the area. It’s essential to monitor weather forecasts and warnings to stay informed about potential flooding. During a flood event, swift action is necessary. If evacuation is advised, it’s important to follow evacuation orders promptly and to have an emergency kit ready with essential supplies. Avoiding floodwaters is critical due to the risks of contamination, swift currents, and hidden hazards. If trapped by rising waters, moving to higher ground and calling for help is advised. After a flood, returning home only when authorities deem it safe is essential to avoid further danger. Overall, proactive planning, quick response, and adherence to safety guidelines are key to mitigating the risks associated with floods and ensuring personal safety.
Importance of Knowing How to Survive in a Crisis
Knowing what to do in a crisis can be the difference between life and death, safety and danger, or recovery and further harm. It empowers individuals to respond swiftly and effectively, minimizing the impact of emergencies on themselves and others. Preparedness includes understanding how to stay safe, whom to contact for help, and how to provide basic first aid when needed. This knowledge not only boosts personal confidence but also contributes to community resilience by ensuring a coordinated response in times of crisis. Being informed and ready to act ensures that critical moments are managed with clarity and purpose, potentially saving lives and mitigating the severity of emergencies.

Natural Disasters
Natural disaster preparedness is essential for safeguarding lives and minimizing damage when nature strikes unexpectedly. It involves understanding the specific risks in your region, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or wildfires, and developing a plan accordingly. This plan typically includes creating emergency kits with essentials like food, water, medications, and important documents, as well as knowing evacuation routes and shelter locations. Regular drills and staying informed through weather alerts or local authorities further enhance readiness. By preparing in advance, individuals and communities can react swiftly and effectively, reducing vulnerability and ensuring a coordinated response to natural disasters.

Man-Made Disasters
Surviving man-made disasters requires quick thinking and preparedness. Understanding the specific risks involved, such as industrial accidents, terrorist attacks, or civil unrest, is crucial. Preparation includes knowing evacuation procedures, having emergency supplies readily available, and staying informed through reliable sources. During such emergencies, following official instructions and avoiding panic are key. Maintaining communication with loved ones and authorities can also aid in ensuring safety and receiving necessary assistance promptly. By being proactive and aware, individuals can increase their chances of surviving and minimizing harm during man-made disasters.

Civil Unrest
Civil unrest refers to a state of public disturbance, typically characterized by protests, demonstrations, or riots due to social, political, or economic issues. During civil unrest, tensions can escalate quickly, leading to violence, property damage, and threats to public safety. It is important for individuals to prioritize personal safety by avoiding areas of unrest, following guidance from local authorities, and staying informed through credible news sources. Remaining calm, keeping a low profile, and refraining from engaging in confrontations can help mitigate risks during such volatile situations. Community solidarity and cooperation with law enforcement can contribute to restoring peace and stability in affected areas.

Health & Epidemics
Health and epidemics represent significant challenges to public health and societal stability. Epidemics, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, exemplify how infectious diseases can rapidly spread globally, overwhelming healthcare systems and disrupting daily life. They not only threaten individual health but also strain economies and social structures. Effective response measures, including vaccination campaigns, public health interventions, and international cooperation, are crucial in containing epidemics and mitigating their impact. Preparedness and swift, coordinated action are key to minimizing loss of life and restoring stability in the face of health crises.

Technological Disasters
Technological disasters encompass a range of catastrophic events caused by failures or accidents in technological systems. These can include power grid failures, cyber attacks, and transportation accidents like airplane crashes. Such disasters often result in widespread disruption, economic losses, and sometimes loss of life. The complexity and interconnectedness of modern technology amplify their potential impact, necessitating robust prevention measures, emergency response protocols, and continuous improvement in safety standards. Addressing technological disasters requires a combination of regulatory oversight, technological innovation, and preparedness to mitigate risks and enhance resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges.

Humanitarian Crisis
Humanitarian crises are characterized by severe suffering and widespread displacement of populations, often due to conflicts, natural disasters, or systemic failures. These crises profoundly impact vulnerable communities, exacerbating poverty, hunger, and lack of access to essential services such as healthcare and education. The humanitarian response involves a coordinated effort by governments, aid organizations, and international bodies to provide emergency relief, shelter, food, and medical assistance to affected populations. Addressing humanitarian crises requires not only immediate humanitarian aid but also long-term solutions aimed at promoting stability, rebuilding communities, and ensuring the protection of human rights. Effective coordination and solidarity among global partners are essential in mitigating the impact of these crises and supporting the resilience and recovery of affected populations.

Climate Change
Climate change-related disasters pose increasingly severe threats to communities and ecosystems worldwide. These disasters encompass a spectrum of events such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and intensified storms, all exacerbated by rising global temperatures and changing weather patterns. They result in profound socio-economic and environmental impacts, including food and water insecurity, displacement of populations, biodiversity loss, and damage to infrastructure. Mitigating and adapting to these disasters requires urgent global action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance resilience in vulnerable regions, and promote sustainable practices. International cooperation, scientific research, and policy innovation are crucial in addressing the root causes and impacts of climate change-related disasters, safeguarding future generations from their devastating consequences.
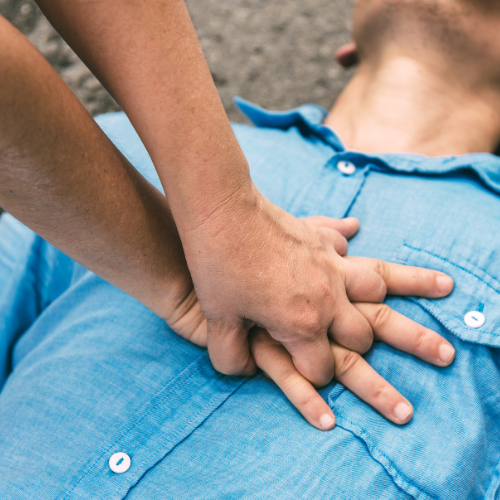

First Aid Administration
First aid encompasses a variety of essential skills and techniques aimed at providing immediate assistance to individuals who have been injured or suddenly become ill. Key areas covered include assessing and managing emergencies such as cuts, burns, fractures, and cardiac arrest. Basic life support techniques like cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) are also part of first aid training. Additionally, first aid protocols address common medical conditions like choking, allergic reactions, seizures, and heat-related illnesses. By learning these skills, individuals are empowered to intervene effectively in emergencies before professional medical help arrives, potentially saving lives and reducing the severity of injuries.

